Design Technology
Design Technology Curriculum Statement
What Design & Technology look like in Goodrich CE (VC) Primary School
At Goodrich Church of England Primary School, we work as a school community to share knowledge, skills and understanding required now and for the future to help each individual achieve their potential.
|
CURRICULUM INTENT |
Curriculum Intent Design and Technology is an inspiring, rigorous and practical subject. It encourages children to learn, to think and to intervene creatively to solve problems both as individuals and as members of a team. Using creativity and imagination, children design and make products that solve real and relevant problems within a variety of contexts, considering their own and others’ needs, wants and values. They acquire a broad range of subject knowledge and draw on disciplines such as mathematics, science, engineering, computing and art. Children learn how to take risks, becoming resourceful, innovative, enterprising and capable citizens. Through the evaluation of past and present design and technology, they develop a critical understanding of its impact on daily life and the wider world. High-quality design and technology education makes an essential contribution to the creativity, culture, wealth and well-being of the nation.
What Design & Technology looks like in our school: Our high-quality scheme of work encourages children to look at, evaluate and adapt existing products and systems, working creatively to design their own that solve real and relevant problems within a variety of contexts (for example home, school, leisure, culture, enterprise, industry and the wider environment). Children are introduced to great inventors and designers from around the world who inspire and encourage the children to become innovators and risk-takers. The delivery of our Design and Technology curriculum, along with our whole school values of Achieve, Believe, Care enable our children to develop their skills, understanding and ability. Above all, we want our children to enjoy their Design and Technology lessons and embrace the opportunities they are presented with, without fear of failure or judgement from others.
This is our philosophy: At Goodrich CE (VC) Primary School we believe Design and Technology should be fully inclusive to every child. Our progressive scheme of work develops children’s skills and knowledge in design, structures, mechanisms, electrical control and a range of materials, including food. We aim to, whenever possible, make cross-curricular links to Maths, English and Science and other compulsory subjects on the curriculum, in a fun manner, putting these subjects into context, making them easier to digest and more understandable.
This is the knowledge and understanding gained at each stage. By the end of EYFS children will:
By the end of Key Stage 1 children will:
By the end of KS2 children will:
|
|
CURRICULUM IMPLEMENTATION |
Curriculum Implementation
This is how it works:
This is what the adults do:
This is how we support the children:
This how we support staff:
This is how we challenge children:
This is how we ensure all children can access the curriculum:
What is Cultural Capital? The National Curriculum defines cultural capital as: ‘the essential knowledge that children need to be educated citizens, introducing them to the best that has been thought and said and helping to engender an appreciation of human creativity and achievement’. This powerful knowledge can be split into two categories: powerful subject knowledge and powerful personal knowledge.
Powerful Subject Knowledge in Design and Technology:
Powerful Personal Knowledge in Design and Technology:
|
|
CURRICULUM IMPACT |
Curriculum Impact The impact of children’s progress and their ability to know more and remember more will be visible through a range of methods. These may include end of unit assessments or quizzes, hot and cold tasks, spoken responses, progress over time in children’ books, extended writing or even an end of unit project.
This is what you might typically see:
This is how we know how well our children are doing:
This is the impact of the teaching: We have identified substantive and disciplinary knowledge which is fundamental to the children’s development and understanding as technicians. They accumulate this as they move through our school which then gives them a firm foundation to build on when they move on to KS3 and beyond.
|
Design Technology Progression Document
|
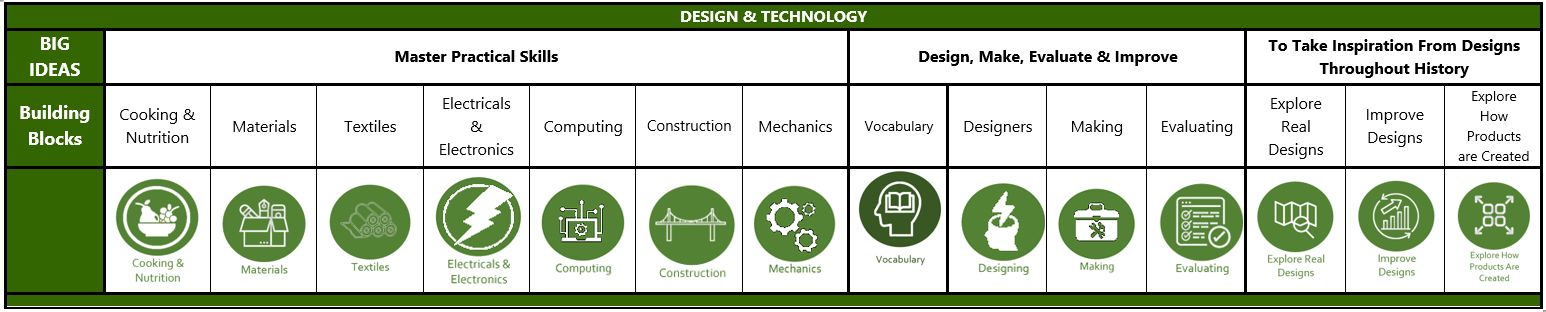
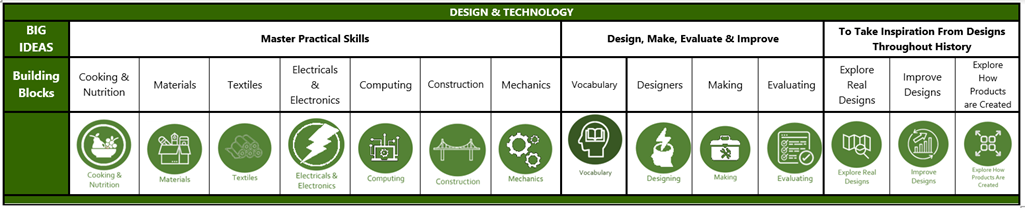
BIG IDEAS |
BUILDING BLOCKS |
EYFS |
MILESTONE 1
|
MILESTONE 2 |
MILESTONE 2 |
|
|
MASTER PRACTICAL SKILLS
|
|
Characteristics of Effective Learning
Early Learning Goals
|
KS1 - use the basic principles of a healthy and varied diet to prepare dishes understand where food comes from. |
KS2 - Understand and apply the principles of a healthy and varied diet. Prepare and cook a variety of predominantly savoury dishes using a range of cooking techniques. Understand seasonality and know where and how a variety of ingredients are grown, reared, caught and processed. |
||
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
DESIGN, MAKE, EVALUATE & IMPROVE
|
|
Year 1 - I can give my opinions on a product. Year 2 - I can say what I like and dislike about the product and the designer.
|
Year 3 - I can talk about some of the tools, techniques used by the designer. Year 4 - I can explain why a product is appealing |
Year 5 - I can give reasons for the decisions made by the designer. Year 6 – I can start to think of new products and |
||
|
|
KS1 - Design purposeful, functional, appealing products for themselves and other users based on design criteria. Generate, develop, model and communicate their ideas through talking, drawing, templates, mock-ups and, where appropriate, information and communication technology. |
KS2 - Use research and develop design criteria to inform the design of innovative, functional, appealing products that are fit for purpose, aimed at particular individuals or groups generate, develop, model and communicate their ideas through discussion, annotated sketches, cross- sectional and exploded diagrams, prototypes, pattern pieces and computer- aided design. |
||||
|
Objectives:
Year 1 - can think of ideas and with help can put I know what a design is. I can use pictures and words to describe what I want to do.
Year 2 - can think of ideas and with help can put them into practice. I know what a design is and its purpose. I can use pictures and words to describe what I want to do (materials, techniques, features, mechanics and tools).
|
Objectives:
Year 3 - I can think of ideas and plan what to do next, based on what I know about materials and components. I can select tools, techniques and I can explain my choices giving reasons.
Year 4 - I can think of ideas and plan what to do next, based on what I know about materials and components. I can select the appropriate tools, techniques and materials explaining my choices. I can communicate my ideas using labelled I can produce step by step plans.
|
Objectives:
Year 5 - can use my knowledge of design, designers and further research to help. I can create models to show aspects of my design.
Year 6 - I can use my knowledge of design, designers and further research to help influence my own design. I can create models or prototypes to show aspects of my design. I can produce step by step plans. I can use computer aided design. I can come up with solutions to problems as they happen.
|
||||
|
|
|
MAKE: Select from and use a range of tools and equipment to perform practical tasks [for example, cutting, shaping, joining and finishing] select from and use a wide range of materials and components, including construction materials, textiles and ingredients, according to their characteristics. Technical knowledge: Build structures, exploring how they can be made stronger, stiffer and more stable. Explore and use mechanisms [for example, levers, sliders, wheels and axles], in their products.
|
MAKE: select from and use a wider range of tools and equipment to perform practical tasks [for example, cutting, shaping, joining and finishing], accurately select from and use a wider range of materials and components, including construction materials, textiles and ingredients, according to their functional properties and aesthetic qualities . Technical knowledge:
|
|||
|
|
KS1 - evaluate their ideas and products against design criteria. |
KS2 - evaluate their ideas and products against their own design criteria and consider the views of others to improve their work.
|
||||
|
Objectives:
Year 1 - I can talk about my own work (features, design, opinion). I describe how my product works Year 2 - I talk about my own and others’ work (features, design, opinion). I can explain why I chose certain materials, techniques and tools. I describe how my product works |
Objectives:
Year 3 - talk about my own and others’ work (features, design, opinion). I can explain why I chose certain materials, techniques and tools. I can say what I would do to improve my product. Year 4 - II can identify what is working well and what can be improved (this is during the make as well as at the end).
|
Objectives:
Year 5 - can reflect on my designs and develop them bearing in mind the way they will be used (during the process). Year 6 - I can reflect on my designs and adapt them based on testing and a prototype.
|
||||
|
TO TAKE INSPIRATION FROM DESIGNS THROUGHOUT HISTORY |
|
|
KS1 - Explore and evaluate a range of existing products.
|
KS2 - Understand how key events and individuals in design and technology have helped shape the world. |
||
|
Objectives:
Year 1 - I know what a designer does.
Year 2 – I know the names and products of some British designers. |
Objectives:
Year 3 - know some designers from history. Year 4 - I know some international designers.
|
Objectives:
Year 5 - I can compare and contrast the work of Year 6 - know how key events and individuals have influenced the world (in terms of products). |
||||
|
|
KS1 - Explore and evaluate a range of existing products. |
KS2 - Investigate and analyse a range of existing products |
||||
|
Objectives:
Year 1 – I know what a product is. I can say what a product is for. I can describe a product (who is it for, Year 2 – I know the features of familiar products. I can give reasons for some features
|
Objectives:
Year 3 - I can start to research and evaluate existing products. I understand that products are designed Year 4 - I can research and evaluate existing products to inform me in my own planning. I understand that products are designed for a purpose (e.g. a problem, an audience, an event).
|
Objectives:
Year 5 - can research and evaluate existing products giving reasons for the decisions of the designers (materials, design, tools, techniques). I can use the ideas from current designers to help me with my own. Year 6 - can research and evaluate existing products giving reasons for the decisions of the designers (materials, design, tools, techniques). I can adapt the ideas from current designers to help me with my own.
|
||||
|
|
||||||
Design Technology Sticky Knowledge
|
Milestone |
Master Skills Mastering practical skills Technical knowledge |
Design, Make, Evaluate and Improve Evaluating Existing and Their Own Products Design and Making |
Take Inspiration From Designs Throughout History |
|
EYFS |
They can find new ways to do things and test their ideas in order to solve a problem
|
They can use their senses to explore the world around them through the engagement of open-ended activities. They can plan and decide how to approach a task, solve problems and reach a finished goal. They can check how well the task is going and make changes if it is needed.
|
They can show curiosity about objects, events and people and can ask/answer questions about why things happen. |
|
1
|
Through practical application, they can use a range of tools/equipment, materials and components according to their characteristics in food, materials, textiles, electrics and electronics, computing, construction, mechanics. |
They can describe a product. They can give reasons for some of its features. They can think of an idea and put it into practice with some help. They can talk about and describe features of their product. |
They can explain what a designer does and give an opinion about a product. |
|
2
|
Through practical application and exploration, they can use a range of tools/equipment, materials and components according to their characteristics in food, materials, textiles, electrics and electronics, computing, construction, mechanics. |
They can explain about a product and given reasons for its purpose. They can think of an idea and plan what to do using their knowledge of materials and components. They can identify what is working well in their design and what needs to be improved so that the product can be used as intended. |
They can recall some designers, and can they explain why a product is appealing to its consumer. |
|
3
|
Through practical application and exploration, they can use a range of tools/equipment, materials and components according to their functional properties and aesthetic qualities in food, materials, textiles, electrics and electronics, computing, construction, mechanics. |
They can explain about a product giving reasons for decisions made by the designer from research and the evaluation of existing products. They can think of an idea and plan what to do using their knowledge of designs, designers and further research which influences their own design. They can reflect on their design and make adaptions so that the product can be used as intended. |
They can recall some designers and explain how decisions are the about the products they make. |
Design Technology Vocabulary
|
Design Technology |
|||||
|
Milestone 1 |
Milestone 2 |
Milestone 3 |
|||
|
axel cut design hinge join joining lever made make measure
|
neat rolling scissors stitch strong tidy tools turning wheels work |
accuracy bake boil column designer evaluate folding hacksaw healthy hygienic
|
measure mechanics mixing product properties purpose scoring structure utensil |
affordable appropriate commercial components connections desirable durable embroidery experiment features
|
influence ingredients plaiting research strength structural technique template visual weaving |